10 Self Control Wheelchair Tips All Experts Recommend
페이지 정보

본문
Types of self propelled wheelchairs for sale Control Wheelchairs
self propelled wheelchair ebay-control wheelchairs are utilized by many disabled people to move around. These chairs are ideal for everyday mobility and are able to easily climb hills and other obstacles. The chairs also feature large rear shock-absorbing nylon tires that are flat-free.
 The speed of translation of wheelchairs was calculated using a local field potential approach. Each feature vector was fed to a Gaussian encoder which output an unidirectional probabilistic distribution. The evidence accumulated was used to trigger the visual feedback, and a command was delivered when the threshold was attained.
The speed of translation of wheelchairs was calculated using a local field potential approach. Each feature vector was fed to a Gaussian encoder which output an unidirectional probabilistic distribution. The evidence accumulated was used to trigger the visual feedback, and a command was delivered when the threshold was attained.
Wheelchairs with hand-rims
The kind of wheels a wheelchair has can affect its mobility and ability to maneuver various terrains. Wheels with hand-rims reduce wrist strain and increase comfort for the user. Wheel rims for wheelchairs may be made from aluminum, plastic, or steel and come in different sizes. They can be coated with rubber or vinyl for improved grip. Some are equipped with ergonomic features like being designed to fit the user's natural closed grip, and also having large surfaces that allow for full-hand contact. This lets them distribute pressure more evenly and reduce the pressure of the fingers from being too much.
Recent research has shown that flexible hand rims can reduce the force of impact as well as wrist and finger flexor actions during wheelchair propulsion. They also provide a larger gripping surface than standard tubular rims, which allows the user to exert less force while still retaining the stability and control of the push rim. These rims are available at a wide range of online retailers as well as DME providers.
The study revealed that 90% of the respondents were pleased with the rims. It is important to keep in mind that this was an email survey of those who purchased hand rims from Three Rivers Holdings, and not all terrain self propelled wheelchair uk wheelchair users suffering from SCI. The survey didn't measure any actual changes in the severity of pain or symptoms. It simply measured the extent to which people noticed an improvement.
The rims are available in four different designs, including the light, big, medium and the prime. The light is a round rim with smaller diameter, and the oval-shaped medium and large are also available. The rims that are prime are a little bigger in diameter and have an ergonomically-shaped gripping surface. The rims can be mounted on the front wheel of the wheelchair in various colours. These include natural, a light tan, and flashy greens, blues, reds, pinks, and jet black. They are also quick-release and can be easily removed for cleaning or maintenance. The rims have a protective rubber or vinyl coating to prevent the hands from sliding off and causing discomfort.
Wheelchairs with a tongue drive
Researchers at Georgia Tech developed a system that allows people who use wheelchairs to control other electronic devices and maneuver it by moving their tongues. It is comprised of a tiny magnetic tongue stud, which transmits movement signals to a headset that has wireless sensors and the mobile phone. The smartphone converts the signals into commands that control the device, such as a wheelchair. The prototype was tested with disabled people and spinal cord injury patients in clinical trials.
To test the performance of this device, a group of physically able people utilized it to perform tasks that measured input speed and accuracy. They performed tasks based on Fitts law, which included keyboard and mouse use, and maze navigation tasks using both the TDS and the regular joystick. A red emergency override stop button was included in the prototype, and a companion was present to help users press the button when needed. The TDS performed just as a normal joystick.
In a separate test in another test, the TDS was compared with the sip and puff system. This allows those with tetraplegia to control their electric wheelchairs through sucking or blowing into straws. The TDS completed tasks three times faster and with greater precision, as compared to the sip-and-puff method. The TDS is able to drive wheelchairs more precisely than a person with Tetraplegia who controls their chair using the joystick.
The TDS was able to track tongue position with a precision of less than a millimeter. It also had a camera system that captured a person's eye movements to identify and interpret their motions. Software safety features were also included, which verified the validity of inputs from users twenty times per second. Interface modules would automatically stop the wheelchair if they did not receive an appropriate direction control signal from the user within 100 milliseconds.
The next step for the team is testing the TDS on people who have severe disabilities. To conduct these trials they have formed a partnership with The Shepherd Center which is a major care hospital in Atlanta and the Christopher and Dana Reeve Foundation. They are planning to enhance their system's sensitivity to lighting conditions in the ambient, to include additional camera systems, and to enable the repositioning of seats.
Joysticks on wheelchairs
With a power wheelchair equipped with a joystick, users can operate their mobility device with their hands without having to use their arms. It can be positioned in the middle of the drive unit, or on either side. It can also be equipped with a display to show information to the user. Some screens have a large screen and are backlit for better visibility. Some screens are smaller, and some may include symbols or images that aid the user. The joystick can be adjusted to accommodate different hand sizes and grips, as well as the distance of the buttons from the center.
As technology for power wheelchairs has evolved and improved, clinicians have been able to create and customize alternative driver controls to enable patients to maximize their ongoing functional potential. These advances also enable them to do this in a way that is comfortable for the end user.
For instance, a typical joystick is an input device with a proportional function which uses the amount of deflection in its gimble to produce an output that increases with force. This is similar to the way that accelerator pedals or video game controllers work. However this system requires motor function, proprioception, and finger strength to be used effectively.
A tongue drive system is a second kind of control that makes use of the position of a user's mouth to determine which direction in which they should steer. A magnetic tongue stud relays this information to a headset, which executes up to six commands. It can be used by those with tetraplegia or quadriplegia.
Certain alternative controls are simpler to use than the traditional joystick. This is particularly beneficial for users with limited strength or finger movements. Others can even be operated by a single finger, which makes them ideal for those who can't use their hands at all or have limited movement.
Additionally, certain control systems come with multiple profiles which can be adapted to the needs of each user. This is particularly important for a new user who might require changing the settings periodically in the event that they feel fatigued or have an illness flare-up. It is also useful for an experienced user who wants to alter the parameters that are initially set for a particular environment or activity.
Wheelchairs with steering wheels
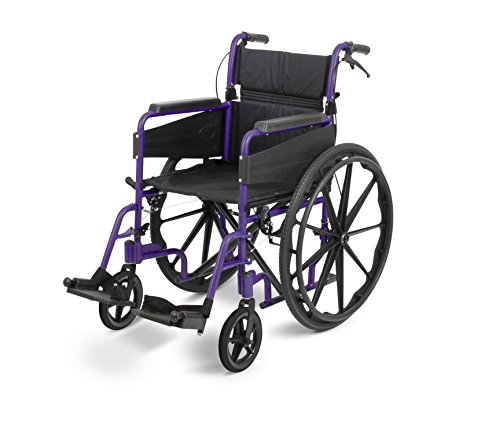
Self-propelled wheelchairs are made for those who need to move themselves on flat surfaces and up small hills. They feature large wheels on the rear for the user's grip to propel themselves. They also have hand rims which allow the individual to use their upper body strength and mobility to control the wheelchair in either a either direction of forward or backward. self propelled wheelchairs uk-ultra lightweight self propelled wheelchair wheelchairs come with a wide range of accessories, including seatbelts, dropdown armrests and swing away leg rests. Certain models can be converted to Attendant Controlled Wheelchairs, which allow caregivers and family to drive and control wheelchairs for users who require more assistance.
To determine the kinematic parameters, participants' wheelchairs were equipped with three wearable sensors that monitored movement throughout an entire week. The gyroscopic sensors that were mounted on the wheels and one fixed to the frame were used to measure the distances and directions of the wheels. To discern between straight forward movements and turns, the period of time during which the velocity differs between the left and right wheels were less than 0.05m/s was considered to be straight. The remaining segments were examined for turns, and the reconstructed wheeled pathways were used to calculate turning angles and radius.
A total of 14 participants took part in this study. The participants were tested on navigation accuracy and command latencies. Through an ecological experiment field, they were tasked to navigate the wheelchair through four different ways. During the navigation trials, sensors monitored the movement of the wheelchair across the entire route. Each trial was repeated twice. After each trial participants were asked to pick a direction in which the wheelchair was to move.
The results revealed that the majority of participants were capable of completing the navigation tasks, although they did not always follow the proper directions. On average 47% of turns were correctly completed. The other 23% were either stopped immediately following the turn or wheeled into a subsequent turning, or replaced by another straight movement. These results are comparable to the results of previous studies.
self propelled wheelchair ebay-control wheelchairs are utilized by many disabled people to move around. These chairs are ideal for everyday mobility and are able to easily climb hills and other obstacles. The chairs also feature large rear shock-absorbing nylon tires that are flat-free.
 The speed of translation of wheelchairs was calculated using a local field potential approach. Each feature vector was fed to a Gaussian encoder which output an unidirectional probabilistic distribution. The evidence accumulated was used to trigger the visual feedback, and a command was delivered when the threshold was attained.
The speed of translation of wheelchairs was calculated using a local field potential approach. Each feature vector was fed to a Gaussian encoder which output an unidirectional probabilistic distribution. The evidence accumulated was used to trigger the visual feedback, and a command was delivered when the threshold was attained.Wheelchairs with hand-rims
The kind of wheels a wheelchair has can affect its mobility and ability to maneuver various terrains. Wheels with hand-rims reduce wrist strain and increase comfort for the user. Wheel rims for wheelchairs may be made from aluminum, plastic, or steel and come in different sizes. They can be coated with rubber or vinyl for improved grip. Some are equipped with ergonomic features like being designed to fit the user's natural closed grip, and also having large surfaces that allow for full-hand contact. This lets them distribute pressure more evenly and reduce the pressure of the fingers from being too much.
Recent research has shown that flexible hand rims can reduce the force of impact as well as wrist and finger flexor actions during wheelchair propulsion. They also provide a larger gripping surface than standard tubular rims, which allows the user to exert less force while still retaining the stability and control of the push rim. These rims are available at a wide range of online retailers as well as DME providers.
The study revealed that 90% of the respondents were pleased with the rims. It is important to keep in mind that this was an email survey of those who purchased hand rims from Three Rivers Holdings, and not all terrain self propelled wheelchair uk wheelchair users suffering from SCI. The survey didn't measure any actual changes in the severity of pain or symptoms. It simply measured the extent to which people noticed an improvement.
The rims are available in four different designs, including the light, big, medium and the prime. The light is a round rim with smaller diameter, and the oval-shaped medium and large are also available. The rims that are prime are a little bigger in diameter and have an ergonomically-shaped gripping surface. The rims can be mounted on the front wheel of the wheelchair in various colours. These include natural, a light tan, and flashy greens, blues, reds, pinks, and jet black. They are also quick-release and can be easily removed for cleaning or maintenance. The rims have a protective rubber or vinyl coating to prevent the hands from sliding off and causing discomfort.
Wheelchairs with a tongue drive
Researchers at Georgia Tech developed a system that allows people who use wheelchairs to control other electronic devices and maneuver it by moving their tongues. It is comprised of a tiny magnetic tongue stud, which transmits movement signals to a headset that has wireless sensors and the mobile phone. The smartphone converts the signals into commands that control the device, such as a wheelchair. The prototype was tested with disabled people and spinal cord injury patients in clinical trials.
To test the performance of this device, a group of physically able people utilized it to perform tasks that measured input speed and accuracy. They performed tasks based on Fitts law, which included keyboard and mouse use, and maze navigation tasks using both the TDS and the regular joystick. A red emergency override stop button was included in the prototype, and a companion was present to help users press the button when needed. The TDS performed just as a normal joystick.
In a separate test in another test, the TDS was compared with the sip and puff system. This allows those with tetraplegia to control their electric wheelchairs through sucking or blowing into straws. The TDS completed tasks three times faster and with greater precision, as compared to the sip-and-puff method. The TDS is able to drive wheelchairs more precisely than a person with Tetraplegia who controls their chair using the joystick.
The TDS was able to track tongue position with a precision of less than a millimeter. It also had a camera system that captured a person's eye movements to identify and interpret their motions. Software safety features were also included, which verified the validity of inputs from users twenty times per second. Interface modules would automatically stop the wheelchair if they did not receive an appropriate direction control signal from the user within 100 milliseconds.
The next step for the team is testing the TDS on people who have severe disabilities. To conduct these trials they have formed a partnership with The Shepherd Center which is a major care hospital in Atlanta and the Christopher and Dana Reeve Foundation. They are planning to enhance their system's sensitivity to lighting conditions in the ambient, to include additional camera systems, and to enable the repositioning of seats.
Joysticks on wheelchairs
With a power wheelchair equipped with a joystick, users can operate their mobility device with their hands without having to use their arms. It can be positioned in the middle of the drive unit, or on either side. It can also be equipped with a display to show information to the user. Some screens have a large screen and are backlit for better visibility. Some screens are smaller, and some may include symbols or images that aid the user. The joystick can be adjusted to accommodate different hand sizes and grips, as well as the distance of the buttons from the center.
As technology for power wheelchairs has evolved and improved, clinicians have been able to create and customize alternative driver controls to enable patients to maximize their ongoing functional potential. These advances also enable them to do this in a way that is comfortable for the end user.
For instance, a typical joystick is an input device with a proportional function which uses the amount of deflection in its gimble to produce an output that increases with force. This is similar to the way that accelerator pedals or video game controllers work. However this system requires motor function, proprioception, and finger strength to be used effectively.
A tongue drive system is a second kind of control that makes use of the position of a user's mouth to determine which direction in which they should steer. A magnetic tongue stud relays this information to a headset, which executes up to six commands. It can be used by those with tetraplegia or quadriplegia.
Certain alternative controls are simpler to use than the traditional joystick. This is particularly beneficial for users with limited strength or finger movements. Others can even be operated by a single finger, which makes them ideal for those who can't use their hands at all or have limited movement.
Additionally, certain control systems come with multiple profiles which can be adapted to the needs of each user. This is particularly important for a new user who might require changing the settings periodically in the event that they feel fatigued or have an illness flare-up. It is also useful for an experienced user who wants to alter the parameters that are initially set for a particular environment or activity.
Wheelchairs with steering wheels
Self-propelled wheelchairs are made for those who need to move themselves on flat surfaces and up small hills. They feature large wheels on the rear for the user's grip to propel themselves. They also have hand rims which allow the individual to use their upper body strength and mobility to control the wheelchair in either a either direction of forward or backward. self propelled wheelchairs uk-ultra lightweight self propelled wheelchair wheelchairs come with a wide range of accessories, including seatbelts, dropdown armrests and swing away leg rests. Certain models can be converted to Attendant Controlled Wheelchairs, which allow caregivers and family to drive and control wheelchairs for users who require more assistance.
To determine the kinematic parameters, participants' wheelchairs were equipped with three wearable sensors that monitored movement throughout an entire week. The gyroscopic sensors that were mounted on the wheels and one fixed to the frame were used to measure the distances and directions of the wheels. To discern between straight forward movements and turns, the period of time during which the velocity differs between the left and right wheels were less than 0.05m/s was considered to be straight. The remaining segments were examined for turns, and the reconstructed wheeled pathways were used to calculate turning angles and radius.
A total of 14 participants took part in this study. The participants were tested on navigation accuracy and command latencies. Through an ecological experiment field, they were tasked to navigate the wheelchair through four different ways. During the navigation trials, sensors monitored the movement of the wheelchair across the entire route. Each trial was repeated twice. After each trial participants were asked to pick a direction in which the wheelchair was to move.
The results revealed that the majority of participants were capable of completing the navigation tasks, although they did not always follow the proper directions. On average 47% of turns were correctly completed. The other 23% were either stopped immediately following the turn or wheeled into a subsequent turning, or replaced by another straight movement. These results are comparable to the results of previous studies.
- 이전글15 Reasons You Shouldn't Be Ignoring Ultra Lightweight Self Propelled Wheelchair 24.11.24
- 다음글You'll Never Guess This Used Self Propelled Wheelchair's Tricks 24.11.24
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.